

| Prev | Advanced Operations Guide | Next |
Pervasive.SQL Database Tasks
The following are the tasks for the Maintain Named Databases dialog:
- To create, modify or delete a Pervasive named database
- To create a bound database
- To modify a named database
- To delete a named database
For conceptual information on named databases, see Pervasive.SQL Database Concepts
To create, modify or delete a Pervasive named database
- In Pervasive Control Center, right-click on Configuration for the database engine that you want to work with.
- Choose Maintain named database from the pop-up menu. The Maintain named database dialog box appears.
Figure 1-1 Maintain Named Database Wizard Dialog Box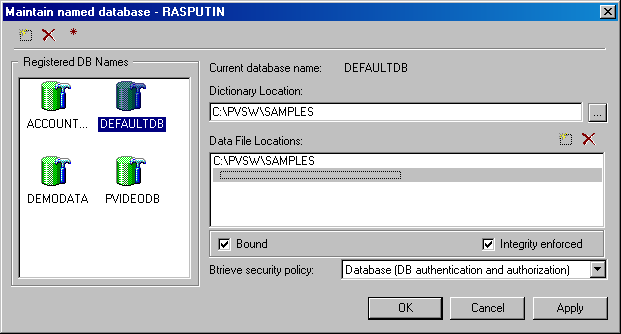
Table 1-7 describes the elements in the Maintain named database dialog box.
Creating a New Bound Database
- Right-click on the Configuration namespace node of the machine on which the named database is to be created.
- Choose Maintain named database from the pop-up menu. The Maintain named database dialog box appears.
Figure 1-2 Maintain Named Databases Dialog Box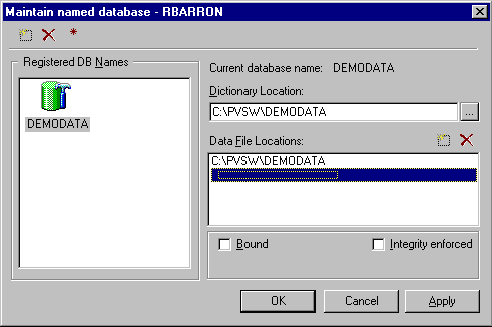
- Click on the Add database icon in the upper left hand corner of the dialog box. A new named database appears in the Registered DB Names panel with its name highlighted. Type in a name for the new database, making sure not to use any spaces.
- Specify the location for the database in the Dictionary Location field. This location must be on the same server to which you are connected (and where the database engine is running). It must be formatted as though you are working directly at the server machine.
- For NetWare, enter a path in the form vol
:\path.- For Windows NT, enter a path in the form drive:\path, where drive is a drive letter on the server.
- For Linux, enter the standard Linux path format from root.
For example, if you are at a workstation connected to a Windows server where the database engine is running, and you want to create a new database on the C:\ drive of the server in the folder "mydata," you would enter the location as "c:\mydata." You would enter it this way even if you have a local network drive (for example, F:\) mapped to the server's C:\ drive.
- Specify the location of the data file(s) in the Data File Locations field. Click on the Add File Location icon just above the directory list or click on the next available blank line in the list.
If you are specifying paths to data file(s) on this server, specify them in the same manner as in the Dictionary Location field (step 4). If you are entering paths to data files on another server, specify the full UNC path as shown below.
- For NetWare, enter the path in the form
\\server\vol:\path- For Windows NT, enter the path in the form \\server\sharename\path
- For Linux, enter the path in one of two ways:
\\server\share\pathor\\server\$PVSW$\pathYou can select a data file path in the list and press the Delete file location icon if you decide not to include a specific data file location.
- Select Bound to bind this database, if desired. For more information on this setting, see Interactions Between Btrieve and Relational Constraints .
- Select Integrity enforced to enforce integrity constraints (security, referential integrity, and triggers) on this database, if desired. For more information on this setting, see Interactions Between Btrieve and Relational Constraints .
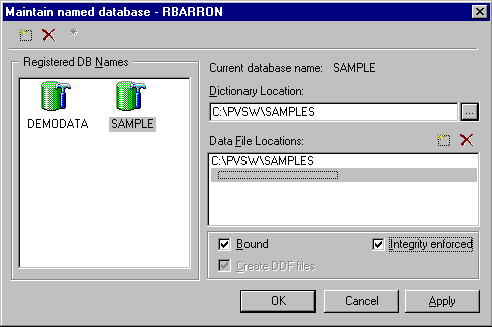
- Select Create DDF Files.
Note
The only situation in which you would choose not to create DDF files is when you have an unnamed legacy database for which DDFs already exist, and you are now creating a database name for that database. Under these circumstances, the database engine links the new database name with the pre-existing DDFs.
Modifying Named Databases
- Click on the database name in the Registered DB Names list.
- Add or modify the named database attributes.
- Click Apply.
Deleting Named Databases
- Click on the database name in the Registered DB Names list.
- Click on the Delete database icon. You can also right-click on the database name and select Delete from the pop-up menu.
Note
Deleting a Named Database without deleting the corresponding DSN(s) results in "orphaned" DSNs. Because the underlying database has been removed, these DSNs do not work. You should always remove any DSNs created for a Named Database if you delete the Named Database.
| Prev Pervasive.SQL Database GUI Reference |
Contents Up Check for Revisions | Next Concepts of Database Maintenance |