

| Prev | User's Guide | Next |
Accessing Data via ODBC From Other Applications
This section explains how to access data using Microsoft Access and Microsoft Excel.
The examples covered in this section are:
Before You Begin
Does the Database Have a DSN Available?
- If you are connecting from a client workstation or from a Workgroup workstation to a server, you must have a Client DSN defined on your workstation for the given remote database. Information on how to create a Client DSN is provided in Setting Up Client Access .
- If you have a Workgroup engine installed on your computer, you may have an Engine DSN defined on your computer for either local or remote databases. Information on how to create an Engine DSN is provided in Setting Up Database Access on Windows .
Note
The instructions in this section apply only to Pervasive.SQL V8, not to previous versions.
Accessing Data Using Microsoft Excel
To access Pervasive data using Excel
- You must have the Pervasive.SQL client or any version of the Pervasive.SQL engine installed on the computer where you are using Excel.
- Start Excel.
- From the Data menu, choose:
Get External Data4New Database Query as shown below.
Figure 2-30 Accessing Pervasive Data using Microsoft Excel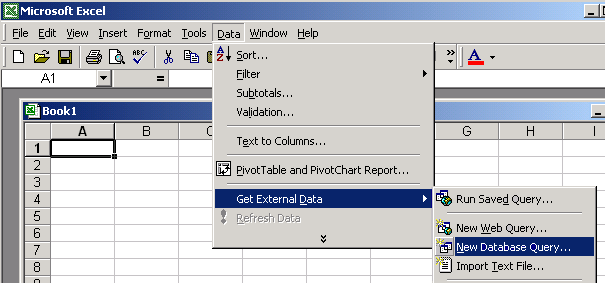
- The Choose Data Source box lists the defined data sources for any ODBC drivers that are installed on your computer. From this list, click on the Client or Server DSN for the Pervasive database you wish to access, as shown in the example below.
Figure 2-31 Excel Display of ODBC Source List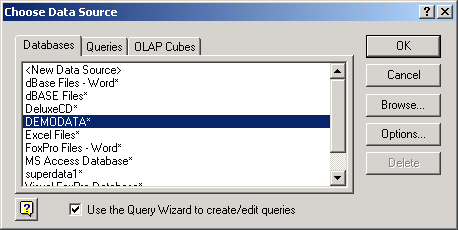
If the database you want does not appear in the ODBC Source list, seeBefore You Begin .
- Click OK. You may be prompted to login to the Pervasive.SQL database. If the database is not secure, leave the User and Password fields empty. Otherwise enter your assigned user name and password.
- The Query Wizard opens. Simply follow the wizard to select your options such as which tables to query, how to filter and sort the data, and how you would like Excel to return the Pervasive data to you for your use.
Accessing Data Using Microsoft Access
To access data from Microsoft Access
- Open Microsoft Access.
- From the Access dialog box, choose Blank Access database as shown below. Click OK. (Note that you may also add Pervasive.SQL tables to an existing Access database.)
Figure 2-32 Create a New Database using Microsoft Access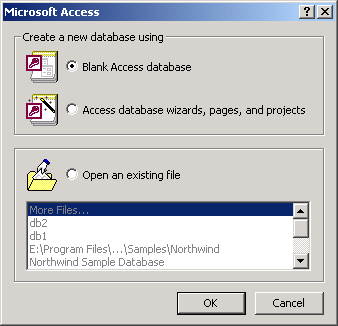
- Next, the File New Database dialog box opens and asks you to name the new database. Name the database and click Create.
- From the Access menu, choose:
File4Get External Data4Link Tables.
Note
You have the option to Import data or Link Tables to the new database. When you choose Import, you break the link to the ODBC data source immediately following the import procedure. Essentially, Import creates a static copy of the data. When you choose Link Tables, Microsoft Access keeps the connection open and remains dependent upon the ODBC data source each time the data is accessed. This way, the data you see reflects any changes to the data at its source.
Note
If you wish to link to a file on a local area network, make sure to use a universal naming convention (UNC) path, instead of relying on the drive letter of a mapped network drive in Windows Explorer. A drive letter can vary on a computer or may not always be defined, whereas a UNC path is a reliable and consistent way for Microsoft Access to locate the data source that contains the linked table.
Figure 2-33 Importing External Data Using Access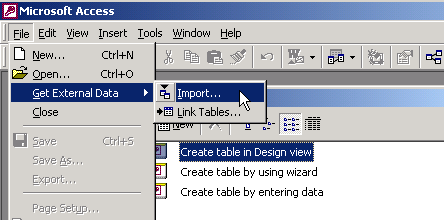
- In the Link dialog box, in the Files Of Type box, select ODBC Databases.
- The Select Data Source box lists the defined data sources for any ODBC drivers that are installed on your computer. Click on the Machine Data Source tab as shown in the figure below.
Figure 2-34 Access Display of ODBC Source List
- Select the ODBC data source that you want to link. If the ODBC data source that you selected requires you to log on, enter your user name and password (additional information might also be required), and then click OK.
Note
To define a new data source for any installed ODBC driver, click New, and then follow the instructions in the Create New Data Source dialog box and the dialog boxes that follow it before proceeding.
Tip
If you are linking a table, select the Save The Login ID And Password check box to store the information for the table in the current database, so that users will not have to enter it each time. If you leave the check box cleared, all users must enter the logon ID and password every time they open the table with Microsoft Access in each new session. Your network administrator can also choose to disable this check box, requiring all users to enter a user name and password each time they connect to the database.
If the database you want does not appear in the ODBC Source list, seeBefore You Begin .
- The Access Link Tables dialog box opens. Click each table that you want to import or link, and then click OK.
Note
Microsoft Access cannot display more than 256 columns in a table. If you need to display more than 256 columns, you may wish to use a different tool.
- Linking to your Pervasive data is complete. As shown in the figure below, Access presents you with options for designing the new database. View the linked tables by double-clicking on the table name.
Figure 2-35 Using Pervasive Data in Microsoft Access
Note
If you are linking a table and it does not have an index that uniquely identifies each record, then Microsoft Access displays a list of the fields in the linked table. Click a field or a combination of fields that will uniquely identify each record, and then click OK.
| Prev Setting Up Client Access |
Contents Up Check for Revisions | Next Deleting DSNs |